For designers
How crack widths affect bond behaviour
To achieve permanent corrosion protection, it is necessary to limit the crack widths in the grout body to < 0.1mm. Proof of this has been furnished by way of extensive bond tests on TITAN injection piles excavated for inspection purposes., with measurement of crack widths, and by comparative calculations.
The different strains in the steel tendon and the cement are compensated for microcracks starting at every rib. Radial microcracks < 0.1mm wide are regarded as insignificant in terms of corrosion and bond. The cracked grout body gives rise to a tension-stiffening effect.
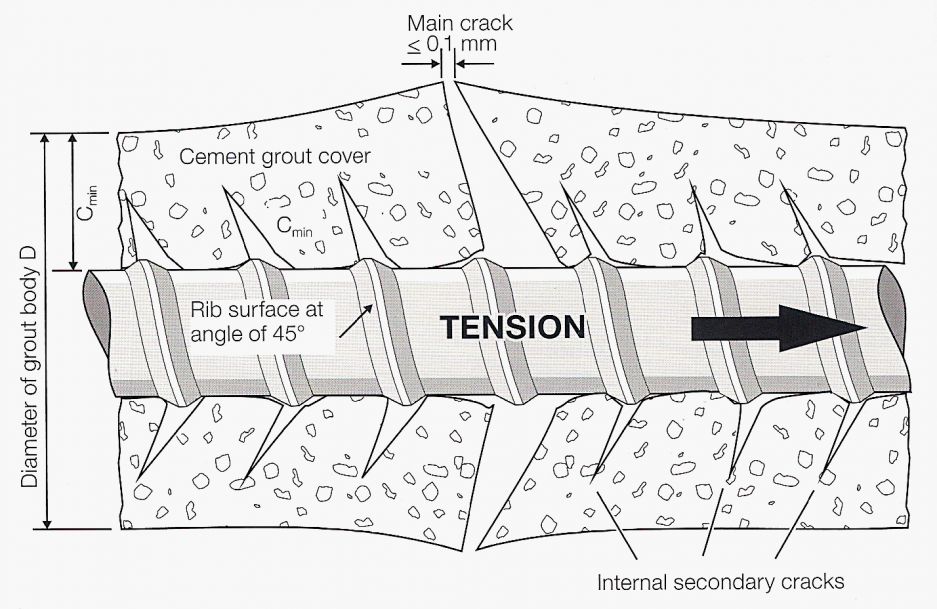
Grout body around TITAN 30/11 injection pile broken away to show completed crack pattern:
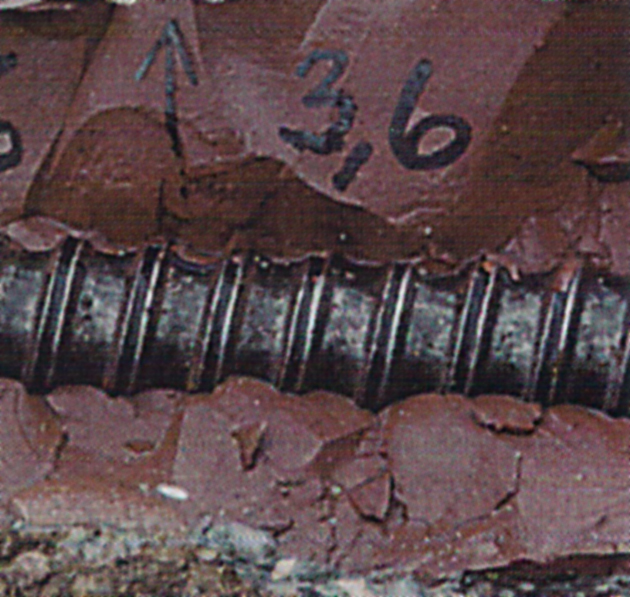

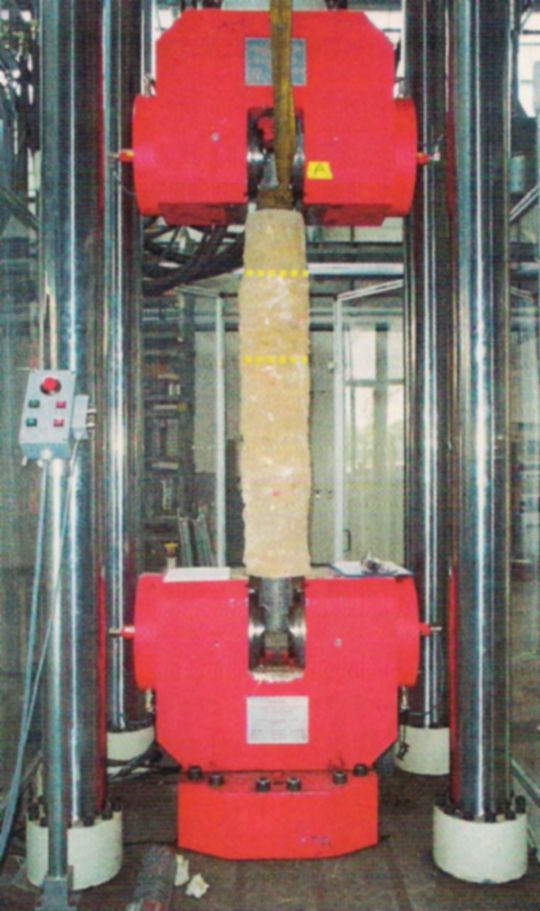
Bond tests with measurement of crack widths on excavated TITAN anchor piles/micropiles, Munich TU :
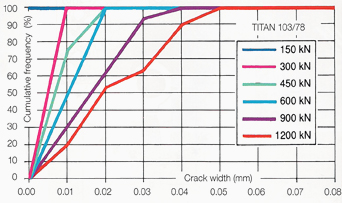
To achieve permanent corrosion protection, it is necessary to limit the crack widths in the grout body to < 0.1mm. Proof of this has been furnished by way of extensive bond tests on TITAN injection piles excavated for inspection purposes., with measurement of crack widths, and by comparative calculations.
The different strains in the steel tendon and the cement are compensated for microcracks starting at every rib. Radial microcracks < 0.1mm wide are regarded as insignificant in terms of corrosion and bond. The cracked grout body gives rise to a tension-stiffening effect.


Bond tests with measurement of crack widths on excavated TITAN anchor piles/micropiles, Munich TU :






 Phone: +371 66 065 303
Phone: +371 66 065 303 E-mail:
E-mail: